July 14, 2023|7 min reading
Artificial intelligence glossary: 70+ terms to know

- Agent: An AI system that can perceive its environment and take actions independently.
- AI alignment: The process of ensuring that AI systems function as intended and align with desired goals.
- Algorithm: Step-by-step instructions that a computer follows to solve a problem or make predictions.
- Anthropomorphism: Attributing human qualities to nonhuman entities, like considering a chatbot as having human characteristics.
- Artificial general intelligence (AGI): AI systems capable of performing any intellectual task that a human can.
- Artificial intelligence (AI): The simulation of human intelligence processes by computer systems.
- Bias: Systematic prejudices that may be present in AI algorithms, leading to biased outcomes.
- Black box AI: AI systems whose inner workings are not easily understandable or explainable.
- ChatGPT: A chatbot developed by OpenAI that generates text responses based on user input.
- Chatbot: An AI-powered tool designed to engage in conversation with users.
- Constitutional AI: Training AI systems to align with a predefined set of values or principles.
- Convolutional neural network (CNN): A type of AI model used for computer vision tasks.
- Corpus: A large collection of written or spoken words used to train language models.
- Copilot: Microsoft's suite of AI-assisted workplace products.
- Cutoff date: The date at which the information used to train an AI model ends.
- Data mining: The process of discovering patterns and extracting useful information from large datasets.
- Data validation: Checking the quality and accuracy of data before using it to train AI models.
- Dall-E: OpenAI's AI-powered image generator that creates images based on textual prompts.
- Deepfake: Convincing AI-generated audio, video, or images that can be used to create deceptive content.
- Deep learning: A subset of machine learning that mimics the way humans learn and acquire knowledge.
- Embodied agents: AI agents with a physical body that perform tasks in the physical environment.
- Emergence: Unpredictable capabilities that arise in AI systems as they become more complex.
- EU AI Act: A regulatory framework for responsible AI deployment in the European Union.
- Expert system: AI systems that simulate the knowledge and behavior of human experts.
- Fréchet inception distance (FID): A metric for evaluating the quality of images generated by AI.
- Garbage in, garbage out (GIGO): The concept that the quality of an AI system's output depends on the quality of its input data.
- Generative adversarial network (GAN): A type of AI model consisting of two neural networks that compete with each other to generate and refine data.
- Generative AI: AI technology that creates new content based on learned patterns in training data.
- Graphics processing unit (GPU): A specialized processor used to accelerate AI computations.
- Generative pre-trained transformer (GPT): A family of AI algorithms, such as GPT-3 and GPT-4, used for natural language processing and generation.
- Hallucination: When an AI system presents false information as if it were true.
- Knowledge engineering: The field of AI that aims to replicate human expertise in specific domains.
- Large language model (LLM): Deep learning algorithms trained on large datasets to understand, summarize, and generate text.
- Large Language Model Meta AI (LLaMA): An open-source large language model released by Meta.
- Machine learning: A branch of AI that enables computers to learn and improve from data without being explicitly programmed.
- Moats: Mechanisms that protect the proprietary aspects of a large language model.
- Model: A trained AI algorithm that can make predictions or perform specific tasks.
- Multimodal AI: AI systems capable of processing and producing output in multiple forms such as text, images, and sound.
- Model collapse: When low-quality generated content contaminates the training set of AI models.
- Natural language generation (NLG): Using AI to generate written or spoken language based on data patterns.
- Natural language processing (NLP): AI's ability to understand and interpret human language.
- Neural network: A network of artificial neurons that process and transmit information, used in deep learning.
- Neuromorphic computing: Computing systems designed to mimic the structure and functioning of the human brain.
- OpenAI: An AI research organization that develops and releases various AI models and technologies.
- Overfitting: When an AI model becomes too specialized in the training data and performs poorly on new, unseen data.
- Parameter: Internal settings learned by an AI model during training that affect its behavior and predictions.
- Prompt: Input provided to an AI system to generate desired output or responses.
- Pathways Language Model (PaLM): Google's transformer-based large language model.
- Prompt engineering: The process of refining prompts to elicit desired output from a large language model.
- Q-learning: A reinforcement learning technique that enables AI models to learn through trial and error.
- Recommendation engine: An AI algorithm that suggests content based on user preferences.
- Reinforcement learning: A machine learning approach where an AI agent learns through interactions and feedback from its environment.
- Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF): Training AI models directly using feedback from humans.
- Sentiment analysis: Analyzing text to determine the underlying sentiment or opinion expressed.
- Supervised learning: Training AI models using labeled data, where the desired outcome is known.
- Speech recognition: AI technology that converts spoken language into text.
- Synthetic data: Computer-generated data used for testing and training AI models.
- Technological singularity: A hypothetical future point where AI surpasses human intelligence, leading to rapid and uncontrollable technological advancement.
- Training data: Data used to train AI models and teach them patterns and behaviors.
- Transformer: A model architecture used for natural language processing, capable of processing context and long-term dependencies in language.
- Turing test: A test to determine if a computer can exhibit human-like intelligence.
- Token: The basic unit of text that an AI model uses to understand and generate language.
- Unsupervised learning: Training AI models on unlabeled data, allowing them to discover patterns and structures on their own.
- Variational autoencoder: A generative AI model used for efficient data coding and signal analysis.
- Zero-shot learning: AI models predicting classes for samples they were not explicitly trained on, based on related knowledge.
Explore more
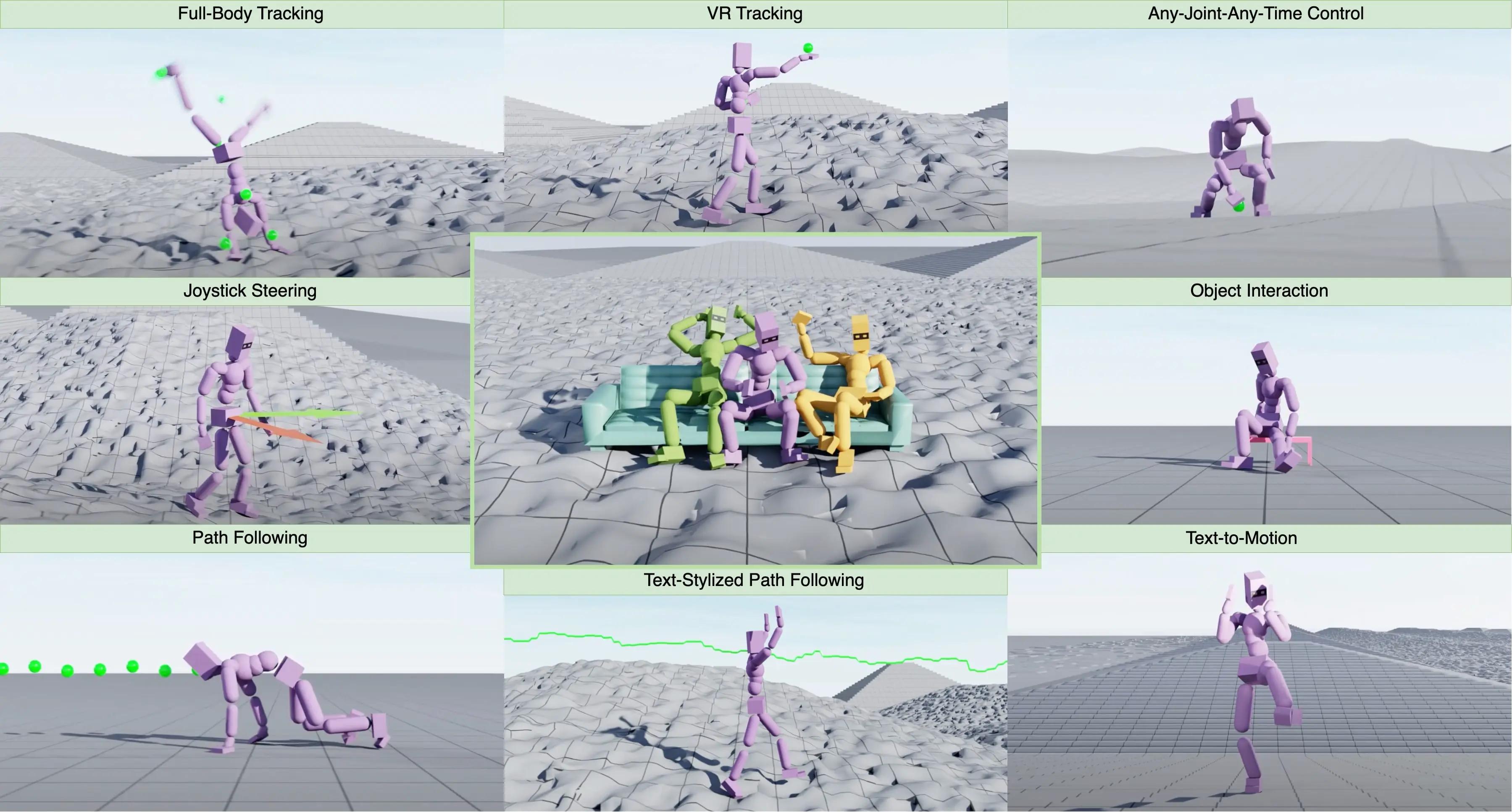
NVIDIA's MaskedMimic: Revolutionizing Physics-Based Character Control
Discover NVIDIA's revolutionary MaskedMimic system for physics-based character control, enabling seamless full-body moti...

Black Forest Labs Launches API for Faster Image Generation with Flux1.1 Pro Model
Black Forest Labs unveils its Flux image generator API, providing developers fast, high-quality image generation options...

Key Points from Apple’s AI Integrations Announced at WWDC 2024
Discover the groundbreaking AI integrations in Apple devices unveiled at WWDC 2024, featuring Apple intelligence, genera...
